Converting Volumes to Meshes with VTK
Introduction
- VTK provides robust tools for generating meshes from volumes, including labelmaps and raw pixel data.
- FlyingEdges3D is a highly efficient algorithm for generating iso-surfaces from volumetric data.
- VTK supports advanced options for mesh optimization, including smoothing and decimation.
Solution to run conversion code automatically
To simplify and unify solutions used in our tutorials, we use Album, a tool for capturing and sharing specific software use cases in dedicated virtual environments.
Click the solution box next to this text and follow the displayed usage instructions to run the solution either from command line or graphical interface.
Conversion of 3D pixel datasets into meshes with VTK
visualization:pixel-volumes-to-meshes-vtk:0.2.0This solution uses vtkFlyingEdges3D to generate meshes from pixel volumes, including optional smoothing and decimation of vertices, and can optionally display the result.
Tags: bioinformatics, neuroscience, data-analysis
Conversion of 3D pixel datasets into meshes with VTK
visualization:pixel-volumes-to-meshes-vtk:0.2.0This solution uses vtkFlyingEdges3D to generate meshes from pixel volumes, including optional smoothing and decimation of vertices, and can optionally display the result.
Tags: bioinformatics, neuroscience, data-analysis
- License: MIT
- Solution creator(s): Deborah Schmidt
album install visualization:pixel-volumes-to-meshes-vtk:0.2.0
album run visualization:pixel-volumes-to-meshes-vtk:0.2.0
--input # (file): Path to the 3D TIFF file containing region data or to a folder containing 3D masks. [Default: ] [Required: Yes]
--output # (directory): Path to the place where the calculated meshes should be stored. [Default: ] [Required: Yes]
--detect_labelmap # (boolean): Process int type images as labelmaps. [Default: 1] [Required: No]
--contour_value # (float): In case continuous datasets are provided, this value can be set to generate meshes at a specific contour value. Otherwise it will be calculated between min and max of the dataset range. [Default: ] [Required: No]
--smoothing_iterations # (integer): Smoothing iterations, usually between 10 and 50. More iterations typically lead to smoother results. Set to 0 to skip smoothing. [Default: 5] [Required: No]
--smoothing_pass_band # (float): Smoothing pass band, determines the amount of smoothing. Lower values result in more smoothing. Usually between 0.0 and 2.0. [Default: 0.5] [Required: No]
--smoothing_feature_angle # (float): The feature angle is the angle between the normals of adjacent polygons. A smaller feature angle will preserve edges. Value in degrees. [Default: 50.0] [Required: No]
--decimate_percentage # (float): How much to decimate vertices after mesh generation (0-1, 0 means do not decimate). [Default: 0.5] [Required: No]
--preserve_topology # (boolean): Preserve topology during mesh decimation. [Default: 0] [Required: No]
--show_meshes # (boolean): Whether to display the generated mesh plots or not. [Default: 0] [Required: No]
--colormap # (string): Name of the matplotlib colormap to use for coloring meshes. [Default: viridis] [Required: No]
--exclude_zero # (boolean): Exclude 0 as a label when processing the volumes. [Default: 1] [Required: No]Cite the following resources if you use this solution:
Dependencies
314 dependencies={'environment_file': """channels:
315 - conda-forge
316dependencies:
317 - python=3.9
318 - pandas=1.5.3
319 - matplotlib-base=3.7.0
320 - numpy=1.24.2
321 - vtk=9.2.6
322 - numpy-stl=3.0.1
323 - opencv=4.8.0
324 - pip
325 - pip:
326 - vtkplotlib==2.1.0
327 - imagecodecs
328 - tifffile==2023.9.26
329"""}Volume conversion using vtkFlyingEdges3D
- Add zero border around dataset
- Load volumetric image using
vtkImageData - Generate meshes using
vtkFlyingEdges3Dalgorithm - Set threshold between foreground and background via
GenerateValues (int numContours, double rangeStart, double rangeEnd)
72 # pad the data to get closed meshes at the border of the image
73 data = np.pad(data, ((1, 1), (1, 1), (1, 1)), 'constant', constant_values=(0,))
74
75 # numpy array to vtk array to vtkImageData
76
77 depth, height, width = data.shape
78 imageData = vtk.vtkImageData()
79 imageData.SetDimensions(width, height, depth)
80 imageData.SetSpacing((1, 1, 1))
81
82 np_dtype = data.dtype
83 vtk_dtype = vtk.VTK_UNSIGNED_CHAR
84 if np_dtype == 'float32':
85 vtk_dtype = vtk.VTK_FLOAT
86 elif np_dtype == 'float64':
87 vtk_dtype = vtk.VTK_DOUBLE
88 elif np_dtype == 'uint8':
89 vtk_dtype = vtk.VTK_UNSIGNED_CHAR
90
91 vtk_array = numpy_support.numpy_to_vtk(num_array=data.ravel(order='C'), deep=True, array_type=vtk_dtype)
92 imageData.GetPointData().SetScalars(vtk_array)
93
94 # apply flying threshold algorithm to generate mesh from volume
95 discrete = vtk.vtkFlyingEdges3D()
96 discrete.SetInputData(imageData)
97 discrete.SetValue(1, contour)
98 discrete.Update()
99
100 next_input = discrete.GetOutput()Smoothing
- Number of iterations: Controls how many smoothing passes are applied.
- Feature Edge Smoothing: Ensures that important edges are preserved while smoothing.
- Boundary Smoothing: Smooths out the mesh along the boundaries.
103 # apply smoothing
104 smoother = vtk.vtkWindowedSincPolyDataFilter()
105 smoother.SetInputData(next_input)
106 smoother.SetNumberOfIterations(smoothing_iterations)
107 smoother.BoundarySmoothingOn()
108 smoother.FeatureEdgeSmoothingOn()
109 smoother.SetFeatureAngle(smoothing_feature_angle)
110 smoother.SetPassBand(smoothing_pass_band)
111 smoother.NonManifoldSmoothingOn()
112 smoother.NormalizeCoordinatesOn()
113 smoother.Update()
114 next_input = smoother.GetOutput()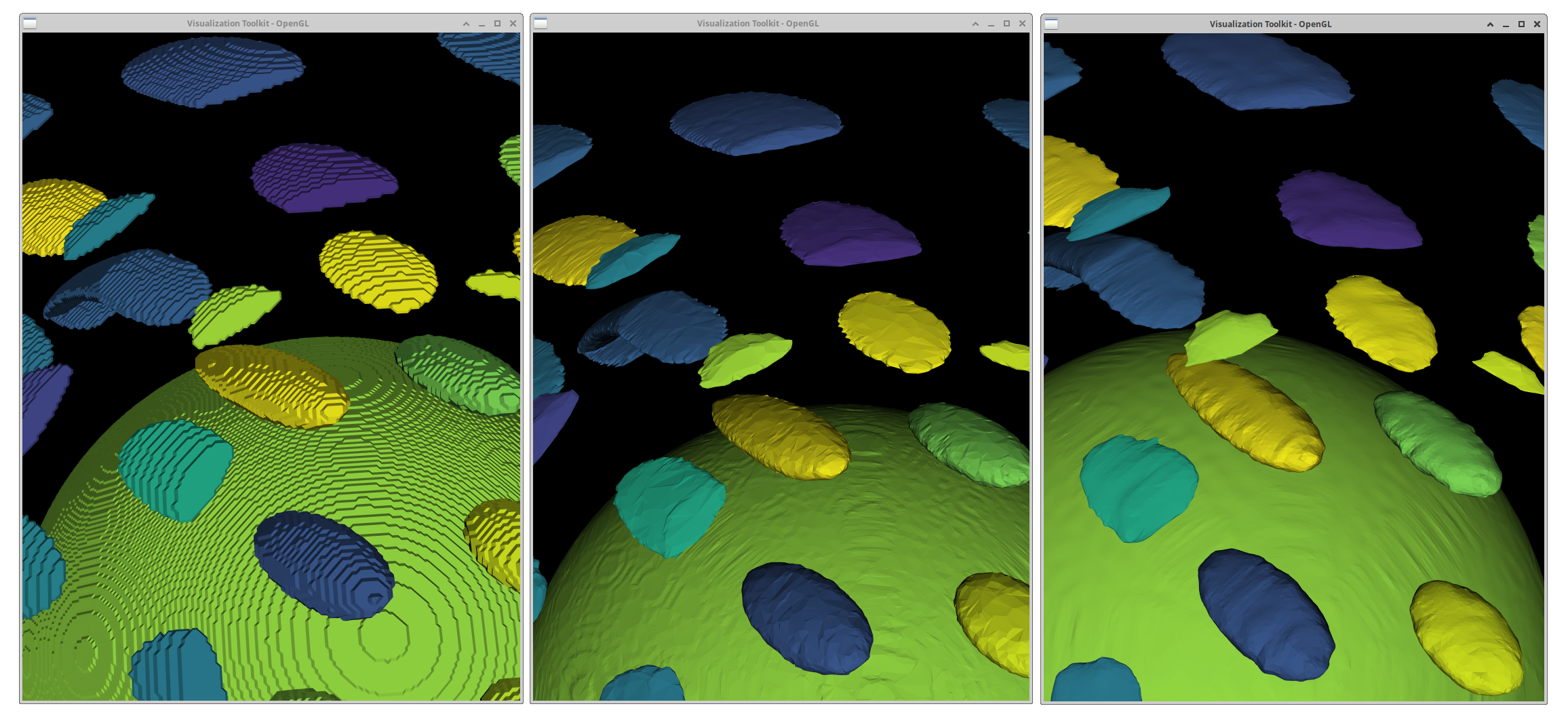
Decimate geometry
- Target Reduction: Defines the percentage reduction in the number of polygons (e.g., 0.5 for 50% reduction).
- Preserve Topology: Ensures that the overall shape and connectivity of the mesh are maintained during decimation.
117 # apply decimation of geometry
118 decimate = vtk.vtkDecimatePro()
119 decimate.SetInputData(next_input)
120 decimate.SetTargetReduction(decimate_percentage)
121 if preserve_topology:
122 decimate.PreserveTopologyOn()
123 decimate.Update()
124
125 next_input = decimate.GetOutput()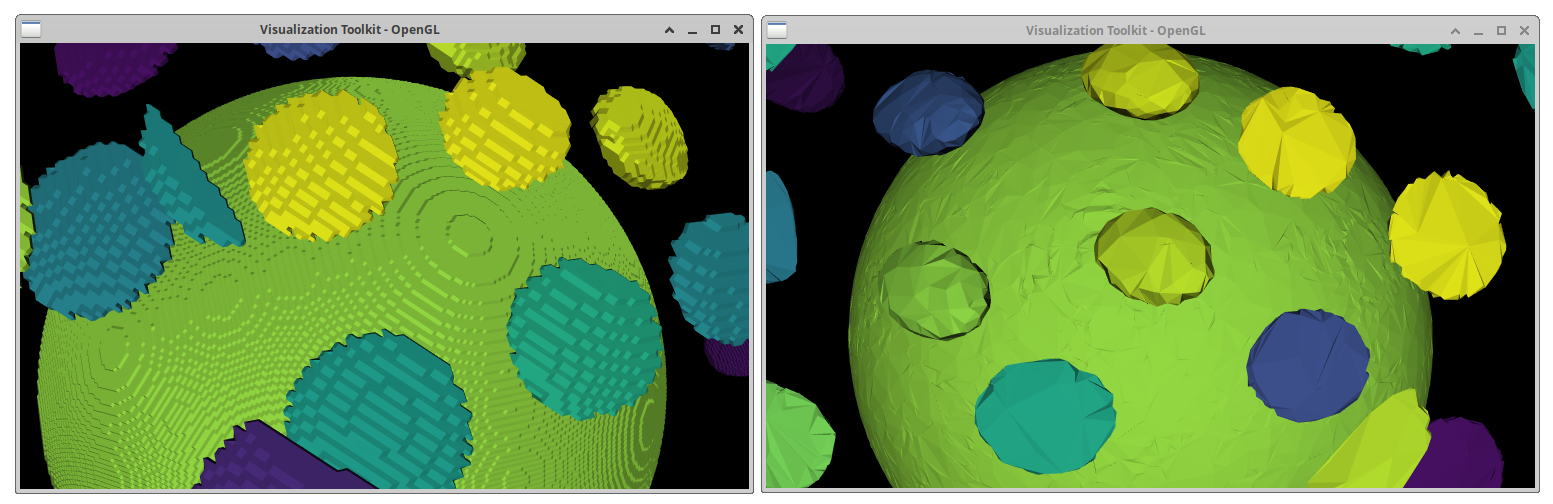
Write STL file
The final step in this process is to write the generated mesh to an STL file. STL files are widely used for 3D printing, simulations, and visualizations in tools like Blender.
155 # write binary STL file
156 writer = vtk.vtkSTLWriter()
157 writer.SetFileName(path)
158 writer.SetInputData(next_input)
159 writer.SetFileTypeToBinary()
160 writer.Write()